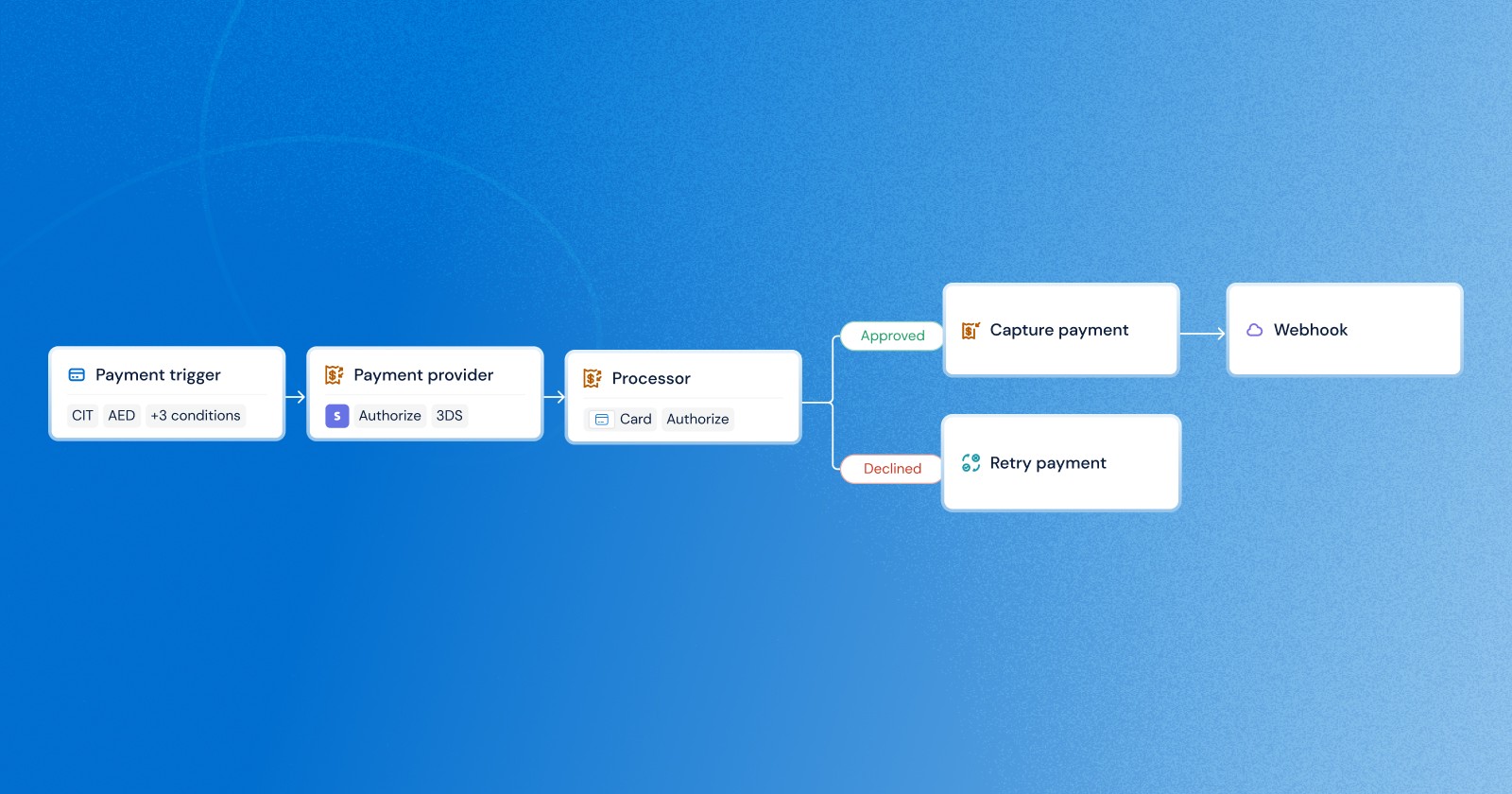
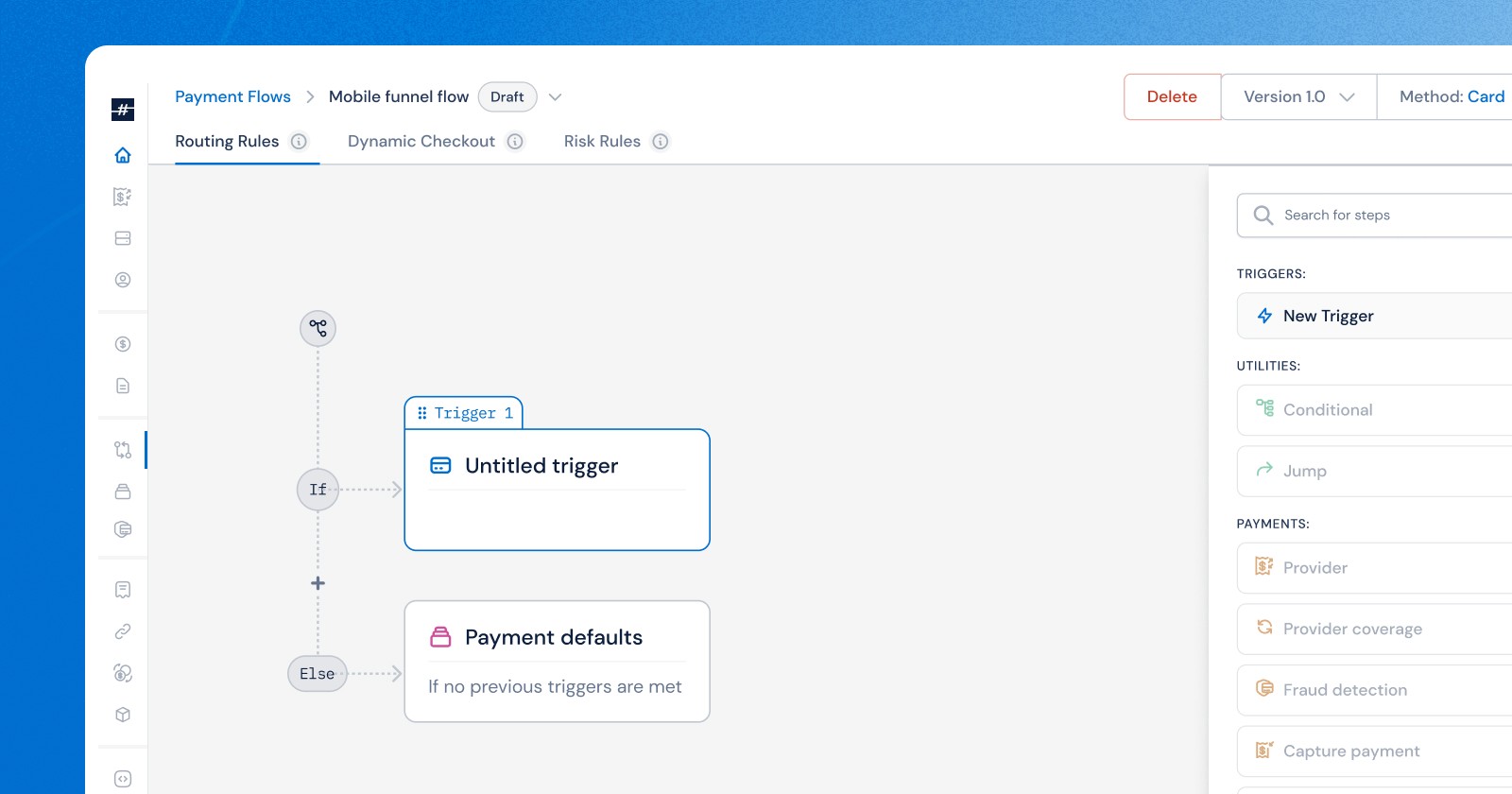
Payment routing is the process of directing transactions through the most suitable and reliable payment provider based on predefined business rules. Rather than forcing all payments through a single provider, businesses have the flexibility of setting payment routing rules that can be optimized for success rates, cost efficiency and operational needs. There are two ways this typically occurs: static routing or dynamic routing.
If you're conducting some research on payment routing and trying to find the best approach for your business, you're in the right place. In this article, we will breakdown dynamic payment routing, how it works, and why it is the right choice for your business when it comes to handling payments at scale. We will also compare static and dynamic routing, discuss the advantages of the latter, and address some of the most frequently asked questions to help you understand how to optimize your payment success.
What is Dynamic Routing?
Dynamic routing in payments (aka “transaction routing”, “smart routing” or “intelligent payment routing”) works like a smart GPS for transactions, it finds the best possible route to ensure a payment is successful. Rather than relying on a single payment processor, it gives merchants the suppleness of directing transactions based on custom rules which improves payment efficiency, reduces failures, lowers cost and enhances overall transaction performance.
Before now, payment routing was manually intensive and required significant technical effort. Merchants had to hardcode payment paths into their backend systems and that meant that any changes; to account for provider outages, to improve success rates or to reduce costs of transactions, would need the help of an engineer or developer. This rigid approach, known as static routing, could not enable the company to respond effectively to the changes in the environment, which led to failed transactions, lost revenue and poor operations.
This is where dynamic routing comes in and changes this by enabling the decision making process to be automated. Unlike the traditional model where merchants are restricted to a single PSP, payment orchestrators like MoneyHash enables them to define their own routing strategies depending on the transaction types, value, currency, payment methods, customers location, risk level and more.
In addition to that, MoneyHash assists merchants with a no-code visual interface to design and manage payment-routing workflows. Using an intuitive drag-and-drop functionality, businesses can easily create and customize numerous routing rules based on key conditions like enabling 3DS, triggering fraud check, considering currencies and so much more. This enables organizations to manage payment operations across different regions, reduce costs, and ensure business continuity during provider downtime without relying on a technical team.
How does dynamic routing actually work?
Let’s explain a bit further: Imagine Mariam, the owner of an international e-commerce store that sells eco-friendly home goods. Her customers are in the KSA, Egypt, and South Africa and they all use different banks, payment methods and currencies. Initially, when Mariam relied on a single global PSP she thought it would take care of all the transactions. But as her business grew, so did the problem of seamless payments:
KSA: Mada Card Failures and Limited BNPL Support
Many Saudi customers used Mada cards which Mariam’s global PSP did not support, resulting in high decline rates and customer churn.
Customers also wanted to use BNPL option for large orders, but her PSP did not support any local providers, which was resulting in lost sales at checkout.
Egypt: High Processing Costs
EGP transactions were made through an international PSP, which was costly in terms of transaction fees and unnecessary currency conversions.
South Africa: Risk and Fraud Issues
Without extra fraud and risk checks, high value transactions were being processed, putting a higher risk on chargebacks and revenue loss.
Fraudulent customers abused refund policies leading to unnecessary disputes and lost revenue
How MoneyHash Helped Through Dynamic Payment Routing
To solve these problems, Mariam integrated several local PSPs through MoneyHash and configured custom payment routing rules using its no-code canvas interface.
In Saudi Arabia: To enhance the approval rates, Mada payments were made to pass through a local PSP. BNPL options were also enabled at checkout for high value SAR transactions to enhance customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
In Egypt: All EGP transactions were processed through a domestic PSP, allowing Mariam to avoid unnecessary conversion fees and greatly minimize the processing costs.
In South Africa: All high value transactions were sent through a fraud detection tool before clearing, and MoneyHash’s risk management rules automatically flagged high-risk transactions, reducing chargebacks and fraud-related losses.
The Results: More efficient payments, better user experience and increased revenue
Static Routing vs. Dynamic Routing
Before diving deeper into more benefits of dynamic routing, let’s take a moment to compare it with static routing, the traditional method of processing payments.
Feature | Static Routing | Dynamic Routing |
|---|---|---|
Routing Logic | Fixed, manually coded paths | Real-time, adaptable paths based on pre-defined rules |
Flexibility | Limited - requires engineer or developer updates | |
Failover Handling | Manual intervention required | Automated fallback to alternative providers |
Optimization Goals | Static - cannot adjust based on conditions | Dynamic - can prioritize cost, success rates, or compliance based on pre-defined rules |
Complexity Management | Difficult to scale across regions | Supports multi-region, multi-currency and multi-method workflows |
Ideal For | Simple, predictable payment flows | Businesses with complex, global payment needs |
What are the Benefits of Dynamic Routing?
Increased Payment Success Rates It is possible to improve the rates of successful payments through automated retries and alternative routing, which are all defined as fallback rules. Dynamic routing allows businesses to:
Configure adaptive retry rules that recover failed payments by retrying on the same provider or dynamically rerouting to another provider when needed (e.g., if PSP1 fails, retry again, then fall back to PSP2)
Set up standards for changing the payment methods in case of an error (e.e., “If a card says ‘insufficient funds,’ then ask for another payment method”).
Implement risk-based routing rules: send high-value transactions through providers with advanced fraud detection, or route flagged transactions to integrated third-party fraud screening before approval (e.g., If transaction value >$2,500 OR risk score >70, then route to PSP1 OR verify via Forter).
Reduced Operational Complexity and Costs The self-service model of dynamic routing reduces the need for the engineer’s involvement in payment management and makes it accessible to non-technical teams. This results in:
Lower engineering costs: No need to alter the code each time there is an update.
Ability to optimize for low cost providers (e.g., “Route all domestic payments through the cheapest local PSP”).
Streamlined operations: Simplify payment processing with dynamic routing, automate provider selection, fraud checks, and post-payment actions, all without engineering effort. (e.g., “If the customer selects Apple Pay, route through Provider A. For card payments, check the BIN: use Provider B for local Egyptian banks to save on fees, otherwise, use Provider C.")
Customizable Payment Workflows Merchants can create payment processes that that are relevant to their business goals rather than using a one-size-fits-all process:
Route transactions by value, currency, location or payment method or any other business condition.
Implement rules for actions before and after the payment, for instance (e.g., "Perform a fraud check for every transaction over $1,000.")
Modify the routing strategy to meet business goals, such as increasing approval rates or minimizing costs.
Business Continuity and Resilience
Merchants can design payment workflows that are unique to their business without being tied to a set process:
Automated fallback to recover transactions based on multiple conditions, such as provider issues, specific error codes, high decline rates, transaction type, or risk assessment, ensuring payments have the best chance of success.
Rules for directing high-risk transactions to providers with effective fraud prevention.
Instant flow adjustments and updates through a no-code interface, enabling quick responses to business requirement or regional compliance updates without technical intervention.
Simplified Management with No-Code Tools
MoneyHash offers a no-code interface, UI based tool for defining and controlling routing rules. This enables businesses to:
Design and revise routing workflows conveniently through drag and drop.
Set conditional rules for fraud checks, 3DS authentication, and any specific actions based on transaction attributes.
Respond quickly to shifting payment environments without having to rely on development resources.
Scalability and Multi-Region Support
Companies can expand their business across various locations and make sure that they are using the proper local payment solutions according to the country’s requirements. This enables:
Routing by customer location to use payment providers that are popular in that area.
Using currency rules to manage the multiple currency transactions correctly.
Compliance with local laws by sorting the transactions to be processed through the region’s specific gateways.
Going the Right Route with MoneyHash
At MoneyHash, we empower businesses to take full control of their payment processes with dynamic, no-code payment routing.
No-Code, Visual Routing
We give you an easy to use, drag and drop interface to design and manage payment workflows, code free – it’s a clean, simple, and organized flow builder.
BIN Routing
Our platform assists you in processing costs and authorization rates by using BIN Lookup and BIN Ranges to move payment flows to specific routes.
Diverse Triggers
We enable you to payment flows in your own way using conditions like Card-on-File, Custom Fields and Country specific rules – these routing triggers are fast with clear conditions.
Volume Split
With us, you can split your transaction volumes across several PSPs, which you can define conditions on to ensure that the load is balanced and performance optimized.
Dynamic 3DS Controls
Our dynamic platform makes it easy for you to determine if 3DS authentication should be enforced or skipped, improving both security and the customer experience.
Automated Fallbacks
We’ve got you covered when a provider goes down, transactions are routed automatically to another pre-set provider, reducing the risk of payment failures.
Integrated Risk Management
You can enhance security by directly incorporating third party fraud checks and risk rules into your payment flows.
Operational Automation and Webhook
We provide webhook support, enabling you to launch real time custom actions across the payment journey and keep your systems in sync.
Version Control and Reporting
We make it easy to see and compare the different versions of your workflows, so that you can see the performance and make changes to to improve it.
The First Step To Future-Proofing Your Business Payments
You’ve made it to the end of this article because you know it’s time to make a decision.
Are you confident that your current payment routing strategy is maximizing success rates?
How much more could you save by dynamically optimizing payment flows?
The right payment orchestration platform doesn’t just process transactions it gives you the flexibility, control, and insights to scale smarter and faster.
At MoneyHash, we help businesses like yours design and automate intelligent payment workflows—without writing a single line of code.
It’s time to future-proof your business, let an expert guide you on the right choice.
Author:
Sanae Rokhou
Senior Product Manager
Technical Product Manager with a focus on simplifying and scaling payment solutions. I combine customer insights with technical knowledge to deliver value-driven products, align cross-functional teams, optimize workflows, and translate complex concepts into user-friendly products.